Gum recession is a common dental problem that occurs when the gum tissue surrounding your teeth pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This can lead to increased sensitivity, a higher risk of tooth decay, and in severe cases, tooth loss. While gum recession often develops gradually, understanding its causes and prevention methods can help you protect your oral health and maintain a confident smile.
What Is Gum Recession?
Gum recession refers to the process where gum tissue wears away, revealing more of the tooth’s surface or root. Healthy gums form a protective barrier around your teeth, but when they recede, this protection diminishes, leaving teeth vulnerable to bacteria and plaque buildup.
Receding gums can occur in people of all ages, though it is more common in adults over 40. However, early detection and proper care can prevent its progression.
Common Causes of Gum Recession
Several factors can contribute to gum recession, including:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup on teeth and along the gumline. Over time, this can harden into tartar, causing gum disease and eventual gum recession.
2. Gum Disease
Gum disease (periodontal disease) is one of the leading causes of gum recession. It’s an infection that damages gum tissue and the supporting structures of the teeth, leading to gum detachment.
3. Aggressive Brushing
Brushing too hard or using a toothbrush with stiff bristles can erode enamel and push gums away from teeth, causing recession over time.
4. Genetics
Some people are genetically predisposed to thinner gum tissue, making them more susceptible to gum recession regardless of their oral care routine.
5. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking and chewing tobacco can impair gum health, reduce blood flow, and increase the risk of gum disease, all of which contribute to recession.
6. Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Grinding or clenching your teeth can exert excessive pressure on your gums, leading to recession.
7. Misaligned Teeth
Crooked or misaligned teeth can create uneven pressure on gums during chewing, leading to gum recession in certain areas.
8. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to recession.
9. Piercings
Oral piercings, such as lip or tongue piercings, can rub against the gums and cause irritation or wear, leading to recession.
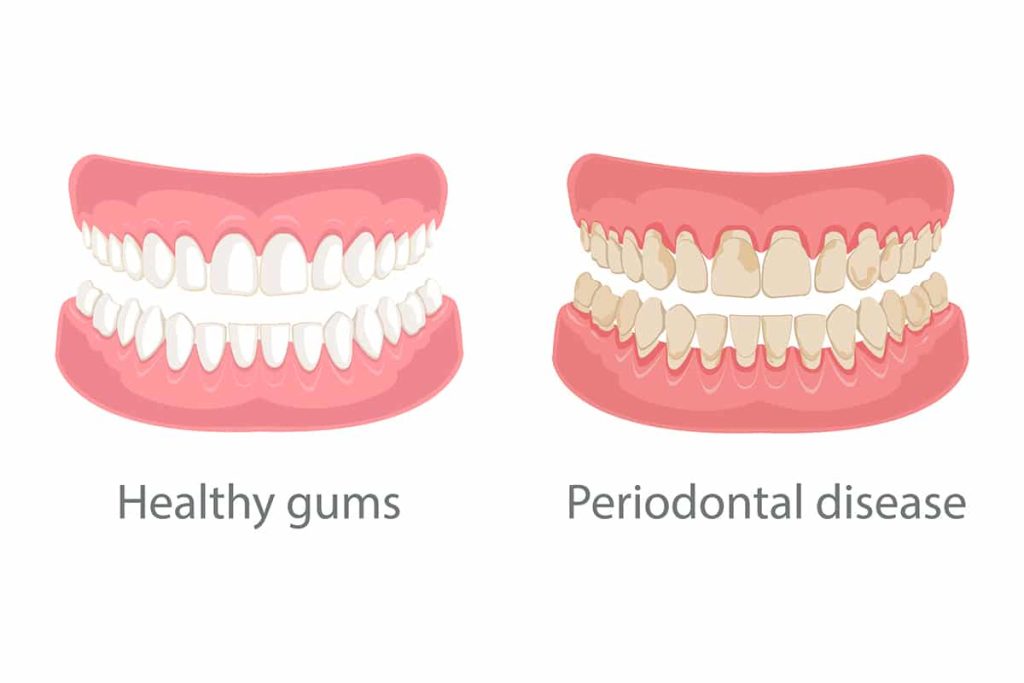
Symptoms of Gum Recession
- Tooth Sensitivity: Pain or discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
- Longer-Looking Teeth: Teeth appear longer as the gumline recedes.
- Exposed Roots: Visible roots can become discolored or sensitive.
- Gum Inflammation: Swollen, red, or bleeding gums may accompany recession.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath due to bacteria buildup.
How to Prevent Gum Recession
Prevention is key when it comes to gum recession. By adopting healthy habits and addressing risk factors, you can maintain strong and healthy gums.
1. Practice Good Oral Hygiene
- Brush your teeth gently twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Use fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel and protect teeth.
- Floss daily to remove plaque from hard-to-reach areas.
2. Avoid Aggressive Brushing
- Use a gentle, circular motion when brushing instead of harsh scrubbing.
- Replace your toothbrush every 3-4 months or when the bristles fray.
3. Treat Gum Disease Early
- Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups to catch gum disease in its early stages.
- Treat any signs of gum inflammation promptly with professional care.
4. Wear a Nightguard
- If you grind your teeth, consider wearing a custom nightguard to prevent damage to your gums and teeth.
5. Stop Smoking
- Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco products can significantly improve gum health.
6. Correct Misaligned Teeth
- Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or Invisalign, can help realign teeth and reduce uneven pressure on gums.
7. Use Mouthwash
- Antibacterial mouthwashes can help reduce plaque and maintain gum health.
8. Protect Your Gums
- If you have oral piercings, be mindful of their contact with gums and consider removing them if irritation persists.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession
If gum recession has already occurred, there are several treatment options available:
1. Scaling and Root Planing
This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline, helping gums reattach to teeth.
2. Gum Graft Surgery
In severe cases, a gum graft can restore lost tissue by taking gum material from another area and attaching it to the affected site.
3. Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST)
A minimally invasive procedure that repositions gum tissue to cover exposed roots without the need for stitches.
4. Desensitizing Products
Special toothpastes or treatments can reduce sensitivity caused by exposed roots.
Conclusion
Gum recession is a progressive condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. By understanding its causes and adopting preventive measures, you can protect your gums and maintain a healthy smile. Regular dental visits are essential for catching early signs of gum issues and ensuring your oral health remains in top condition.
If you’re concerned about gum recession or experiencing symptoms, consult your dentist for a personalized treatment plan. A proactive approach today can save your gums and teeth tomorrow!


